This article is translated from
21 HTML Tips You Must Know About , author: Shefali, with slight modifications.
In this article, I will share 21 HTML tips and code snippets that can improve your coding skills.
Contents
- 1 Link contacts
- 2 Create collapsible content
- 3 Use semantic elements
- 4 form elements
- 5 Enhanced drop-down menu
- 6 Improve video presentation
- 7 Support multi-select drop-down
- 8 Display text as subscript and superscript
- 9 Create download link
- 10 Define the base URL of relative links
- 11 Control image loading
- 12 Control the translation function
- 13 Set maximum input length
- 14 Set minimum input length
- 15 Enable content editing
- 16 Control spell check
- 17 Accessibility
- 18 Set the target behavior of jump links
- 19 Show extensions
- 20 Accept specific file types
- 21 Optimize video loading
- 22 at last
Link contacts
Create clickable email, phone and SMS links using HTML:
<!-- Email link --> < a href = "mailto:name@example.com" > Send Email </ a > <!-- Phone call link --> < a href = "tel:+1234567890" > Call Us </ a > <!-- SMS link --> < a href = "sms:+1234567890" > Send SMS </ a >
Create collapsible content
If you want to include collapsible content on your web page, you can use the <details>and <summary>tags.
<details>Labels create a container for hidden content, while <summary>tags provide a clickable tab to toggle the visibility of that content.
< details > < summary > Click to expand </ summary > < p > This content can be expanded or collapsed. </ p > </ details >
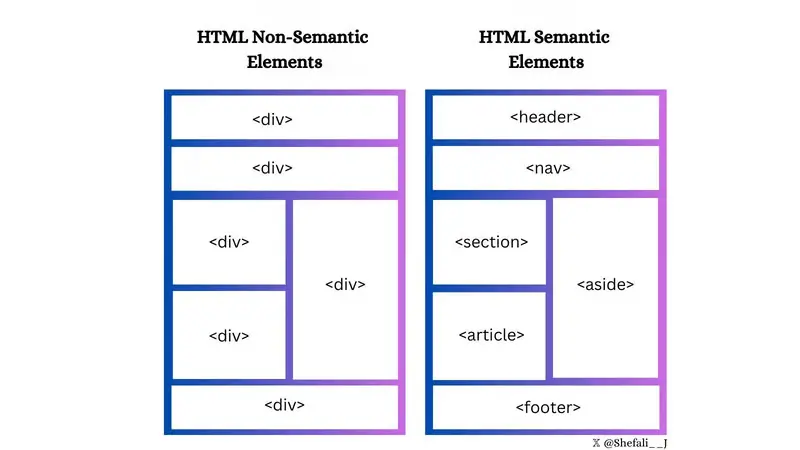
Use semantic elements
Choose semantic elements over non-semantic elements for your website. Make your code more meaningful and improve structure, accessibility, and SEO.
form elements
Use <fieldset>labels to group related elements in your form, and use <legend>labels and <fieldset>tags <fieldset>to define titles for labels.
This is useful for creating more efficient and accessible forms.
< form >
< fieldset >
< legend > Personal details </ legend >
< label for = "firstname" > First name: </ label >
< input type = "text" id = "firstname" name = "firstname" />
< label for = "email" > Email: </ label >
< input type = "email" id = "email" name = "email" />
< label for = "contact" > Contact: </ label >
< input type = "text" id = "contact" name = "contact" />
< input type = "button" value = "Submit" />
</ fieldset >
</ form >
You can use <optgroup>tags to group related options into <select>HTML tags. Use this option when you are working with a large menu or a long list of options.
< select >
< optgroup label = "Fruits" >
< option > Apple </ option >
< option > Banana </ option >
< option > Mango </ option >
</ optgroup >
< optgroup label = "Vegetables" >
< option > Tomato </ option >
< option > Broccoli </ option >
< option > Carrot </ option >
</ optgroup >
</ select >
Improve video presentation
posterProperty can <video>be used with elements to display an image until the user plays the video.
< video controls poster = "image.png" width = "500" > < source src = "video.mp4" type = "video/mp4 /> </video>
Support multi-select drop-down
You can use multipleattributes with the <input>and <select>elements to allow the user to select/enter multiplea value in one go.
< input type = "file" multiple />
< select multiple >
< option value = "java" > Java </ option >
< option value = "javascript" > JavaScript </ option >
< option value = "typescript" > TypeScript < / option >
< option value = "rust" > Rust </ option >
</ select >
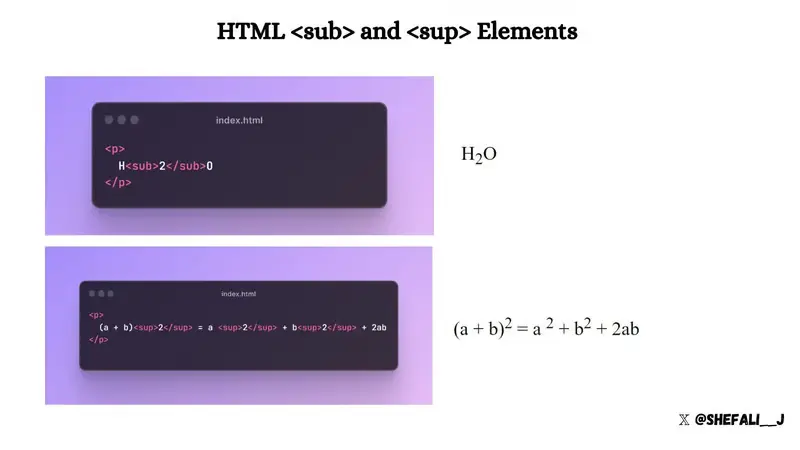
Display text as subscript and superscript
<sub>The and <sup>elements can be used to display text as subscript and superscript respectively.
Create download link
You can use downloadattributes with <a>elements to specify that when a user clicks the link, the linked resource is downloaded without redirecting.
< a href = "document.pdf" download = "document.pdf" > Download PDF </ a >
Define the base URL of relative links
You can use <base>tags to define a base URL for all relative URLs in a web page.
This makes it easier to navigate and load resources when you want to create a shared base URL for all relative URLs on a web page.
< head > < base href = "https://shefali.dev" target = "_blank" /> </ head > < body > < a href = "/blog" > Blogs </ a > < a href = "/ get-in-touch" > Contact </ a > </ body >
Control image loading
Attributes with loadingelements <img>can be used to control how the browser loads the image. It has three values: “eager”, “lazy” and “auto”.
< img src = "picture.jpg" loading = "lazy" >
Control the translation function
You can use translateattributes to specify whether the content of an element should be translated by the browser’s translation feature.
< p translate = "no" > This passage needs no translation. </p>
Set maximum input length
By using maxlengthproperties, you can set the maximum number of characters that users can enter in an input field.
< input type = "text" maxlength = "4" >
Set minimum input length
By using minlengthproperties, you can set the minimum number of characters that users enter in an input field.
< input type = "text" minlength = "3" >
Enable content editing
Use contenteditableattributes to specify whether the content of an element is editable. It allows the user to modify the content within the element.
< div contenteditable = "true" > You can edit this text </div>
Control spell check
You can use spellcheckattributes with <input>elements, content-editable elements, and <textarea>elements to enable or disable the browser’s spell checking.
< input type = "text" spellcheck = "true" />
Accessibility
altProperty specifies alternative text when the image cannot be displayed. Always add descriptive altattributes to images to improve accessibility and SEO.
< img src = "picture.jpg" alt = "Description for the image" >
Set the target behavior of jump links
You can use targetproperties to specify the interaction behavior when a linked resource is clicked.
<!-- This is the default value, opens the link in the current browser window or tab --> < a href = "https://shefali.dev" target = "_self" > Open </ a > <!-- Open the link in a new browser window or tab --> < a href = "https://shefali.dev" target = "_blank" > Open </ a > <!-- Open the link in the parent tab, if one exists --> < a href = "https://shefali.dev" target = "_parent" > Open </ a > <!-- Open the link in a full browser window--> < a href = "https://shefali.dev" target = "_top" > Open </ a > <!-- Custom: If a window or tab with the same name exists, the link will be opened in that window, otherwise a new window or tab will be created --> < a href = "https://shefali. dev" target = "framename" > Open </ a >
Show extensions
titleYou can use attributes to provide additional information about an element when the user hovers over it .
< p title = "World Health Organization" > WHO </ p >
Accept specific file types
You can use acceptproperties to specify the file types that the server accepts (applies to file types only). It <input>is used with elements.
< input type = "file" accept = "image/png, image/jpeg" />
Optimize video loading
You can speed up the loading of video files by using attributes with preloadelements <video>for smoother playback.
< video src = "video.mp4" preload = "auto" > Your browser does not support the video tag. </ video >
at last
This concludes the article I shared today. I hope this 21 HTML tips will be helpful to you. You are welcome to leave a message for more optimization tips you know~
